The Evolution of APT36’s Crimson RAT: Tracking Variants and Feature Expansion Over the Years
“To understand the immeasurable, the mind must be extraordinarily quiet, still.”
— Jiddu Krishnamurti
By Seeker(李标明) China
Independent Malware Analyst & Researcher
Download the Full Report (PDF)
Summary
APT36, also known as The
Transparent Tribe, ProjectM, Mythic Leopard, or Earth Karkaddan, is a cyber
espionage threat organization associated with Pakistan. The organization has
carried out cyber espionage activities against the Indian defense, government,
and education sectors.
Recently I have been
focused on a many-year Crimson
RAT of variants about APT36. It is a very intriguing thing we
can observe: the history of evolution about Crimson RAT variants, which goes
from the basic functionalities to becoming a professional design, which goes
from the simple to the complicated, the below I would like to share with them.
Technique analysis
Crimson RAT V1.0.0.0
At
version 1.0.0.0, I collected three variants; they were named rlbwrarhsa,
drmaiprave, and jivarthr_edis. And compiled in different years, yeah, such as
2019, 2021, and 2023. The basic functionalities are designed as remote access
trojans: upload GIF, download file, delete a file, kill a process, capture
screen, enumerate and exfiltrate processes information, and so on. And the
command's response from the server only used simple string prefix “rlbwrarhsa-“
concatenation, string insertion, and changes to the logic conditions to do
obfuscation for evasion. After all, it uses string comparisons and tries to do
evasion. And the main common feature or skill is using different characters,
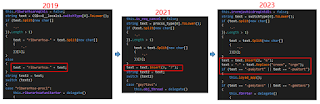
like “| or !,” to split strings to handle obfuscation.
Fig1. Command
obfuscation technique (2019,2021,2023)
The above different variants are very similar, and the structure, the functionalities, the logic, and the design are not to change a lot. I do more detailed work to check them out and make a table to record as follows.
Fig.2 the detailed
functionalities table
Crimson RAT
V2.1.0.0
At version v2.1.0.0, I do research on the name Kosovo; obviously, it is a big change. The structure, the functionalities, the logic, and the design become more complicated. From the below, we can see a more extensive functionalities list on the table, which is shared with different commands in Logic Branch; the structure and the design also become complicated.
Fig.3 the extensive
functionalities
The extensive
functionalities
It’s a surprise that the Crimson RAT variant embedded a command for loading the malware usbworm. Which means it can do lateral movment through removable media like usb. And it’s intent on expanding the surface of attacking and maybe more commands to add for loading other network weapons through the Crimson RAT channel in the future. It shows that APT36 plans to make the basic RAT to support a more integrated technique design.
Fig.4 support usbworm
spreading
Another new finding is developing a functionality for splitting a source file into multiple small files, and in real attacks, it has the requirement for exfiltrating a big file, which may be to evade the traffic detection.
Fig.5 splitting a source
file
In order to confirm if the Crimson RAT is running, it starts a process and checks repeatedly (up to 10 times) whether the application still exists.
Fig.6 check repeatedly
The extensive evasion
techniques
At version 2.1.0.0, the Crimson RAT uses ComputeStringHash to do evasion; it is a compiler-generated method that calculates a hash of a string, which can hide string comparisons and avoid static string detection.
Fig.7 hide string
comparisons with ComputeStringHash
Another evasion
technique for anti-VM/anti-analysis with querying hardware serials like Win32_BaseBoard.SerialNumber
or querying CPU id information.
Fig.8
anti-VM/anti-analysis
The use of a byte array
to store a hostname like richa-sharma.ddns[.]net instead of a plain string as
version 1.0.0.0 is a common evasion technique, and the ddns[.]net is a Dynamic
DNS domain, commonly used by attackers for Command & Control (C2) servers,
as follows:
Fig.9 byte array set by
a Dynamic DNS domain
Conclusion
From the above Crimson
RAT analysis, compare the history variants of both version 1.0.0 and version
2.1.0.0. The APT36 group is also very positive about expanding their abilities
and improving their exclusive network weapons according to the real attack,
from the basic to professional functionalities, from the simple to complicated;
we can see the threat actors are growing. Let’s pay more attention to.
MITRE
ATT&CK TTP Mapping
Crimson RAT V1.0.0.0 (rlbwrarhsa)
MITRE
ATT&CK TTP Mapping
Crimson RAT V2.1.0.0 (Kosovo)
IOCs
Files:
|
Name |
Version |
MD5 |
|
Rlbwrarhsa |
v1.0.0.0 |
8a1f4a512fe9edbcc62ba4b1c3e08f0a |
|
Drmaiprave |
v1.0.0.0 |
77c29d464efcae961424ae050453ef11 |
|
jivarthr_edis |
v1.0.0.0 |
fed22809d70062733cd1c34e16b75c05 |
|
Kosovo |
V2.1.0.0 |
e40e0a71efd051374be1663e08f0dbd8 |
Sha256
ecd7d7a27a2a043919a233bb91e3b009c05b7c81ff132a7c29228e1c45d2b6a6
f5e7b8dddd4137ac008186a4c5e9cb644dc1bbddb61612c29c2087b1efe48974
63f96f77786b8499ce4e08a1883a1d5569563da14b507390cfcbd7b37c5dfb9a
947e75dc1f9b8a6d74a6d55afa7513ed86db907965cf0935ebb26c17f0ec6c5d
Network:
rlbwrarhsa
IP:101[.]155.260.18
Default
Port: 6828
drmaiprave
IP:10[.]105.106.118
Default
Port: 6188
jivarthr_edis
101[.]125.206.108
Default
Port: 6859
Kosovo
richa-sharma.ddns[.]net
Default
Port: 10101
Host:
Kosovo
pdb_path
D:\Projects\Wibemax\Windows RAT\1 Windows 10 Client\Sunny\2022-06-17 Richa\W8P
Sunny\obj\Debug\Kosovo.pdb
Application.StartupPath + "\\exc.txt"
End.
Labels: #APT36, #CrimsonRAT, #MalwareAnalysis, #ThreatIntel












0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home